17.7.7 Packet Tracer – Troubleshoot Connectivity Issues – Physical Mode Answers
Topology
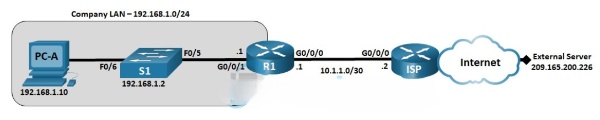
Addressing Table
| Device | Interface | IP Address | Subnet Mask | Default Gateway |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R1 | G0/0/0/1 | 192.168.1.1 | 255.255.255.0 | N/A |
| G0/0/0 | 10.1.1.1 | 255.255.255.252 | N/A | |
| ISP | G0/0/0 | 10.1.1.2 | 255.255.255.252 | N/A |
| Lo0 | 209.165.200.226 | 255.255.255.255 | N/A | |
| S1 | VLAN 1 | 192.168.1.2 | 255.255.255.0 | 192.168.1.1 |
| PC-A | NIC | 192.168.1.10 | 255.255.255.0 | 192.168.1.1 |
Objectives
- Part 1: Identify the Problem
- Part 2: Implement Network Changes
- Part 3: Verify Full Functionality
- Part 4: Document Findings and Configuration Changes
Background / Scenario
In this Packet Tracer Physical Mode (PTPM) activity, the company that you work for is experiencing problems with their LAN. You have been asked to troubleshoot and resolve the network issues. In Part 1, you will connect to devices on the LAN and use troubleshooting tools to identify the network issues, establish a theory of probable cause, and test that theory. In Part 2, you will establish a plan of action to resolve and implement a solution. In Part 3, you will verify that full functionality has been restored. Part 4 provides space for you to document your troubleshooting findings along with the configuration changes that you made to the LAN devices.
Instructions
Part 1: Identify the Problem
The only available information about the network problem is that the users are experiencing slow response times and that they are not able to reach an external device on the internet at IP address 209.165.200.226. To determine probable cause(s) for these network issues, you will need to utilize network commands and tools on the LAN equipment.
Note: The username admin01 with a password of cisco12345 will be required to log on to the network equipment.
Step 1: Troubleshoot the network.
Use the tools available to you to troubleshoot the network, keeping in mind that the requirement is to restore connectivity to the external server and the eliminate slow response times.
Step 2: Document the probable causes.
List the probable causes for the network problems that employees are experiencing.
- The Default Gateway is not set on the PC.
- S1 Interface F0/5 is set to half duplex and speed set to 10.
- S1 default-gateway is set to 192.168.1.0
- R1 G0/0/1 is set to half duplex and the speed is set to 10.
- The gateway of last resort is not set on R1.
Part 2: Implement Network Changes
You have communicated the problems that you discovered in Part 1 to your supervisor. She has approved these changes and has requested that you implement them.
Part 3: Verify Full Functionality
Verify that full functionality has been restored. PC-A, S1, and R1 should be able to reach the external server, and ping replies from PC-A to the external server should exhibit no significant variation in response times.
Part 4: Document Findings and Configuration Changes
Use the space provided below to document the issues found during your troubleshooting and the configurations changes made to resolve those issues.
Documentation will vary but should include the date when troubleshooting was conducted, devices that were tested, commands used along with the output generated by those commands, issues found, and configuration changes made to resolve those issues.
Reflection Question
This Packet Tracer Lab Companion had you troubleshoot all devices before making any changes. Is there another way to apply the troubleshooting methodology?
Answers may vary. Another way the troubleshooting methodology could be applied would be to complete all 6 steps on a device before moving on to another device. For example, after you determined that the default gateway was not set on the PC, you would add the default gateway setting and verify functionality. If network issues still exist, you would then move on to the next device, S1 in this example. When the troubleshooting process had been completed on S1 and issues still existed, you would then move on to R1. This process would continue until full network functionality was achieved.
Device Configs – Final
Switch S1:
enable config terminal no ip domain-lookup hostname S1 ip domain-name ccna-lab.com username admin01 privilege 15 secret cisco12345 interface FastEthernet0/1 shutdown interface FastEthernet0/2 shutdown interface FastEthernet0/3 shutdown interface FastEthernet0/4 shutdown interface FastEthernet0/5 speed 100 duplex full interface Vlan1 ip address 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.0 ip default-gateway 192.168.1.1 banner motd $ Authorized Users Only! $ line vty 0 4 login local transport input ssh line vty 5 15 login local transport input ssh crypto key generate rsa general-keys modulus 1024 end
Router R1:
enable config terminal hostname R1 no ip domain lookup ip domain name ccna-lab.com username admin01 privilege 15 secret cisco12345 interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1 ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 speed 100 duplex full no shutdown interface GigabitEthernet0/0/0 ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.252 no shutdown banner motd $ Authorized Users Only! $ line vty 0 4 login local transport input ssh ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.1.1.2 crypto key generate rsa general-keys modulus 1024 end
Router ISP:
hostname ISP no ip domain lookup interface GigabitEthernet0/0/0 ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.252 no shut interface Lo0 ip address 209.165.200.226 255.255.255.255 ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.1.1.1 end
