11.9.3 Packet Tracer – VLSM Design and Implementation Practice (Answers)
Scenario 1 – Network Address: 10.11.48.0/24
Topology
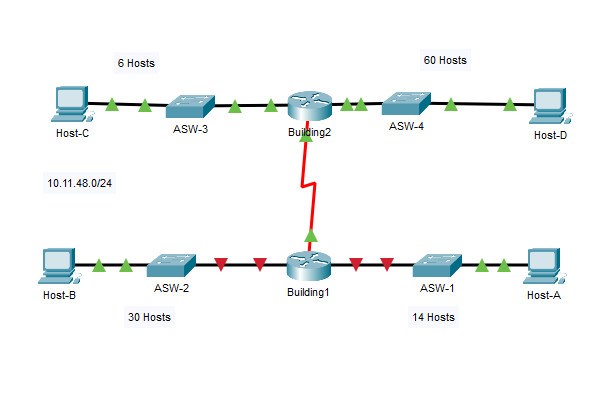
Addressing Table
| Device | Interface | Address | Subnet Mask | Default Gateway |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Building1 | G0/0 | 10.11.48.97 | 255.255.255.240 | N/A |
| G0/1 | 10.11.48.65 | 255.255.255.224 | N/A | |
| S0/0/0 | 10.11.48.121 | 255.255.255.252 | N/A | |
| Building2 | G0/0 | 10.11.48.113 | 255.255.255.248 | N/A |
| G0/1 | 10.11.48.1 | 255.255.255.192 | N/A | |
| S0/0/0 | 10.11.48.122 | 255.255.255.252 | N/A | |
| ASW1 | VLAN 1 | 10.11.48.98 | 255.255.255.240 | 10.11.48.97 |
| ASW2 | VLAN 1 | 10.11.48.66 | 255.255.255.224 | 10.11.48.65 |
| ASW3 | VLAN 1 | 10.11.48.114 | 255.255.255.248 | 10.11.48.113 |
| ASW4 | VLAN 1 | 10.11.48.2 | 255.255.255.192 | 10.11.48.1 |
| Host-A | NIC | 10.11.48.110 | 255.255.255.240 | 10.11.48.97 |
| Host-B | NIC | 10.11.48.94 | 255.255.255.224 | 10.11.48.65 |
| Host-C | NIC | 10.11.48.118 | 255.255.255.248 | 10.11.48.113 |
| Host-D | NIC | 10.11.48.62 | 255.255.255.192 | 10.11.48.1 |
Objectives
Part 1: Examine the Network Requirements
Part 2: Design the VLSM Addressing Scheme
Part 3: Assign IP Addresses to Devices and Verify Connectivity
Background
In this activity, you are given a /24 network address to use to design a VLSM addressing scheme. Based on a set of requirements, you will assign subnets and addressing, configure devices and verify connectivity.
Instructions
Part 1: Examine the Network Requirements
Step 1: Determine the number of subnets needed.
You will subnet the network address 10.11.48.0/24. The network has the following requirements:
- ASW-1 LAN will require 14 host IP addresses
- ASW-2 LAN will require 30 host IP addresses
- ASW-3 LAN will require 6 host IP addresses
- ASW-4 LAN will require 60 host IP addresses
How many subnets are needed in the network topology? 5
Step 2: Determine the subnet mask information for each subnet.
a. Which subnet mask will accommodate the number of IP addresses required for ASW-1?
255.255.255.240/28
How many usable host addresses will this subnet support?
14 (10.11.48.97 – 10.11.48.110)
b. Which subnet mask will accommodate the number of IP addresses required for ASW-2?
255.255.255.224 /27
How many usable host addresses will this subnet support?
30 (10.11.48.65 – 10.11.48.94)
c. Which subnet mask will accommodate the number of IP addresses required for ASW-3?
255.255.255.248 /29
How many usable host addresses will this subnet support?
6 (10.11.48.113 – 10.11.48.118)
d. Which subnet mask will accommodate the number of IP addresses required for ASW-4?
255.255.255.192 /26
How many usable host addresses will this subnet support?
62 (10.11.48.1 – 10.11.48.62)
e. Which subnet mask will accommodate the number of IP addresses required for the connection between Building1 and Building2?
255.255.255.252/30
Part 2: Design the VLSM Addressing Scheme
Step 1: Divide the 10.11.48.0/24 network based on the number of hosts per subnet.
a. Use the first subnet to accommodate the largest LAN.
b. Use the second subnet to accommodate the second largest LAN.
c. Use the third subnet to accommodate the third largest LAN.
d. Use the fourth subnet to accommodate the fourth largest LAN.
e. Use the fifth subnet to accommodate the connection between Building1 and Building2.
Step 2: Document the VLSM subnets.
Complete the Subnet Table, listing the subnet descriptions (e.g. ASW-1 LAN), number of hosts needed, then network address for the subnet, the first usable host address, and the broadcast address. Repeat until all addresses are listed.
Subnet Table
| Subnet Description | Number of Hosts Needed | Network Address/CIDR | First Usable Host Address | Last Usable Host Address | Broadcast Address |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Host-D LAN | 60 | 10.11.48.0/26 | 10.11.48.1 | 10.11.48.62 | 10.11.48.63 |
| Host-B LAN | 30 | 10.11.48.64/27 | 10.11.48.65 | 10.11.48.94 | 10.11.48.95 |
| Host-A LAN | 14 | 10.11.48.96/28 | 10.11.48.97 | 10.11.48.110 | 10.11.48.111 |
| Host-C LAN | 6 | 10.11.48.112/29 | 10.11.48.113 | 10.11.48.118 | 10.11.48.119 |
| WAN Link | 2 | 10.11.48.120/30 | 10.11.48.121 | 10.11.48.122 | 10.11.48.123 |
Step 3: Document the addressing scheme.
a. Assign the first usable IP addresses to Building1 for the two LAN links and the WAN link.
b. Assign the first usable IP addresses to Building2 for the two LAN links. Assign the last usable IP address for the WAN link.
c. Assign the second usable IP addresses to the switches.
d. Assign the last usable IP addresses to the hosts.
Part 3: Assign IP Addresses to Devices and Verify Connectivity
Most of the IP addressing is already configured on this network. Implement the following steps to complete the addressing configuration.
Step 1: Configure IP addressing on the Building1 router LAN interfaces.
Step 2: Configure IP addressing on the ASW-3, switch including the default gateway.
Step 3: Configure IP addressing on Host-D, including the default gateway.
Step 4: Verify connectivity.
You can only verify connectivity from Building1, ASW-3, and Host-D. However, you should be able to ping every IP address listed in the Addressing Table.
Devices configuration – Answer
Building 1
en conf t int g0/0 ip add 10.11.48.97 255.255.255.240 no shut int g0/1 ip add 10.11.48.65 255.255.255.224 no shut
ASW3
en conf t int vlan 1 ip add 10.11.48.114 255.255.255.248 no shut ip def 10.11.48.113
Host-D
IP Address: 10.11.48.62
Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.192
Default Gateway: 10.11.48.1
Download PDF & PKA files
Scenario 2 – Network Address: 172.31.103.0/24
Topology
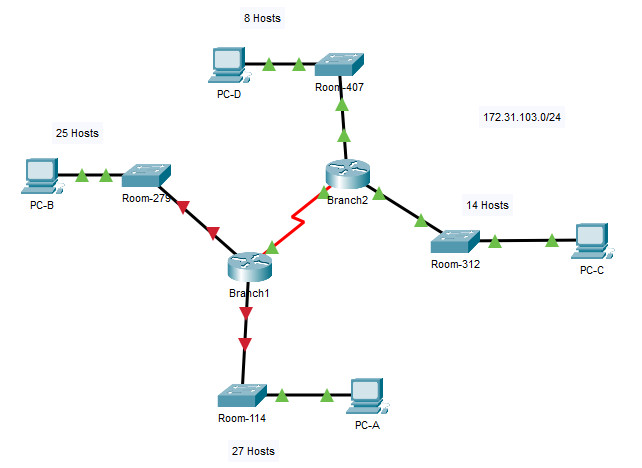
Subnet Table
| Subnet Description | Number of Hosts Needed | Network Address/CIDR | First Usable Host Address | Last Usable Host Address | Broadcast Address |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PC-A LAN | 27 | 172.31.103.0/27 | 172.31.103.1 | 172.31.103.30 | 172.31.103.31 |
| PC-B LAN | 25 | 172.31.103.32/27 | 172.31.103.33 | 172.31.103.62 | 172.31.103.63 |
| PC-C LAN | 14 | 172.31.103.64/28 | 172.31.103.65 | 172.31.103.78 | 172.31.103.79 |
| PC-D LAN | 8 | 172.31.103.80/28 | 172.31.103.81 | 172.31.103.94 | 172.31.103.95 |
| WAN Link | 2 | 172.31.103.96/30 | 172.31.103.97 | 172.31.103.98 | 172.31.103.99 |
| Device | Interface | Address | Subnet Mask | Default Gateway |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Branch1 | G0/0 | 172.31.103.1 | 255.255.255.224 | N/A |
| G0/1 | 172.31.103.33 | 255.255.255.224 | N/A | |
| S0/0/0 | 172.31.103.97 | 255.255.255.252 | N/A | |
| Branch2 | G0/0 | 172.31.103.65 | 255.255.255.240 | N/A |
| G0/1 | 172.31.103.81 | 255.255.255.240 | N/A | |
| S0/0/0 | 172.31.103.98 | 255.255.255.252 | N/A | |
| Room-114 | VLAN 1 | 172.31.103.2 | 255.255.255.224 | 172.31.103.1 |
| Room-279 | VLAN 1 | 172.31.103.34 | 255.255.255.224 | 172.31.103.33 |
| Room-312 | VLAN 1 | 172.31.103.66 | 255.255.255.240 | 172.31.103.65 |
| Room-407 | VLAN 1 | 172.31.103.82 | 255.255.255.240 | 172.31.103.81 |
| PC-A | NIC | 172.31.103.30 | 255.255.255.224 | 172.31.103.1 |
| PC-B | NIC | 172.31.103.62 | 255.255.255.224 | 172.31.103.33 |
| PC-C | NIC | 172.31.103.78 | 255.255.255.240 | 172.31.103.65 |
| PC-D | NIC | 172.31.103.94 | 255.255.255.240 | 172.31.103.81 |
Branch 1
en conf t int g0/0 ip add 172.31.103.1 255.255.255.224 no shut int g0/1 ip add 172.31.103.33 255.255.255.224 no shut
Room-312
en conf t int vlan 1 ip add 172.31.103.66 255.255.255.240 no shut ip def 172.31.103.65
PC-D
IP Address: 172.31.103.94
Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.240
Default Gateway: 172.31.103.81
Download Packet Tracer file
Scenario 3 – Network Address: 192.168.72.0/24
Topology
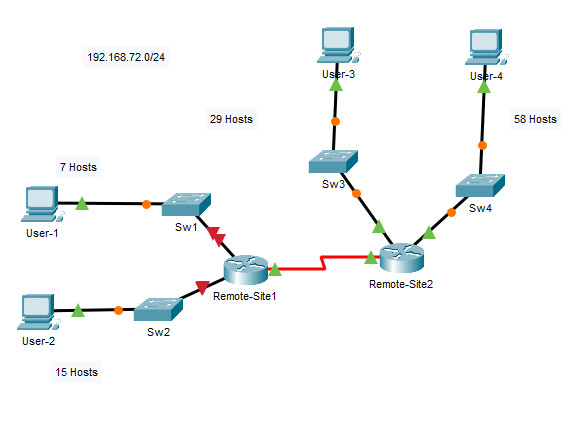
Subnet Table
| Subnet Description | Number of Hosts Needed | Network Address/CIDR | First Usable Host Address | Last Usable Host Address | Broadcast Address |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| User-4 LAN | 58 | 192.168.72.0/26 | 192.168.72.1 | 192.168.72.62 | 192.168.72.63 |
| User-3 LAN | 29 | 192.168.72.64/27 | 192.168.72.65 | 192.168.72.94 | 192.168.72.95 |
| User-2 LAN | 15 | 192.168.72.96/27 | 192.168.72.97 | 192.168.72.126 | 192.168.72.127 |
| User-1 LAN | 7 | 192.168.72.128/28 | 192.168.72.129 | 192.168.72.142 | 192.168.72.143 |
| WAN Link | 2 | 192.168.72.144/30 | 192.168.72.145 | 192.168.72.146 | 192.168.72.147 |
| Device | Interface | Address | Subnet Mask | Default Gateway |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Remote-Site1 | G0/0 | 192.168.72.129 | 255.255.255.240 | N/A |
| Remote-Site1 | G0/1 | 192.168.72.97 | 255.255.255.224 | N/A |
| Remote-Site1 | S0/0/0 | 192.168.72.145 | 255.255.255.252 | N/A |
| Remote-Site2 | G0/0 | 192.168.72.65 | 255.255.255.224 | N/A |
| Remote-Site2 | G0/1 | 192.168.72.1 | 255.255.255.192 | N/A |
| Remote-Site2 | S0/0/0 | 192.168.72.146 | 255.255.255.252 | N/A |
| Sw1 | VLAN 1 | 192.168.72.130 | 255.255.255.240 | 192.168.72.129 |
| Sw2 | VLAN 1 | 192.168.72.98 | 255.255.255.224 | 192.168.72.97 |
| Sw3 | VLAN 1 | 192.168.72.66 | 255.255.255.224 | 192.168.72.65 |
| Sw4 | VLAN 1 | 192.168.72.2 | 255.255.255.192 | 192.168.72.1 |
| User-1 | NIC | 192.168.72.142 | 255.255.255.240 | 192.168.72.129 |
| User-2 | NIC | 192.168.72.126 | 255.255.255.224 | 192.168.72.97 |
| User-3 | NIC | 192.168.72.94 | 255.255.255.224 | 192.168.72.65 |
| User-4 | NIC | 192.168.72.62 | 255.255.255.192 | 192.168.72.1 |
Remote-Site1
en conf t int g0/0 ip add 192.168.72.129 255.255.255.240 no shut int g0/1 ip add 192.168.72.97 255.255.255.224 no shut
Sw-3
en conf t int vlan 1 ip add 192.168.72.66 255.255.255.224 no shut ip def 192.168.72.65
User-4
IP Address: 192.168.72.62
Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.192
Default Gateway: 192.168.72.1
Download Packet Tracer (.pka) file:
